Electroencephalography
 Electroencephalography (EEG) – non-invasive method for studying the functional state of the brain by recording its bioelectric activity. EEG is a sensitive method of research, it reflects the slightest changes in the function of the cerebral cortex and deep brain structures.
Electroencephalography (EEG) – non-invasive method for studying the functional state of the brain by recording its bioelectric activity. EEG is a sensitive method of research, it reflects the slightest changes in the function of the cerebral cortex and deep brain structures.
Electroencephalography enables qualitative and quantitative analysis of the functional state of the brain and its reactions under the action of stimuli. EEG recording is widely used in diagnostic and therapeutic work (especially often in epilepsy), as well as in the study of brain activity related to the implementation of such functions as perception, memory, adaptation etc.
Indications for EEG
- Dynamic control of the functional state of the brain in epilepsy, non-paroxysmal epileptic disorders, with pathogenetically significant organic changes in the brain with neurosis-like symptoms and cognitive impairment;
- detection of signs of structural or microstructural changes in the brain;
- at the request of the patient (without direction).
Biofeedback
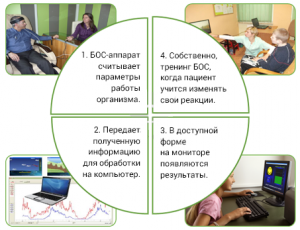
Biofeedback treatment is continuous monitoring in real time certain physiological indicators and conscious management of using multimedia, gaming, and other methods in the specified range of values. In other words, biofeedback interface is for a person a kind of “physiological mirror” that reflects its internal processes.
Biofeedback training based on electroencephalography – neyrobioupravleniya technology, ie, the ability to control brain biopotentials, with the active participation of the person.
EEG biofeedback training is used in medicine, education, sports, and for the treatment of neuro-rehabilitation, correction of psychosomatic disorders, to improve cognitive functions.
Indications for EEG biofeedback training
- Neurosis;
- depression;
- panic attacks;
- hyperactivity and attention disorder;
- problems with learning, without expressed intellectual deviations;
- stuttering;
- developmental disorder of expressive writing;
- tics;
- enuresis;
- headaches;
- the effects of neuroinfections;
- psychosomatic disorders: bronchial asthma, eczema, dermatitis, irritable bowel syndrome, and others.
Cognitive evoked potentials
Cognitive evoked potentials – brain response to a mental task. Allows you to objectify the state of cognitive (mental) processes.
The method is used to study brain functions responsible for cognitive processes. Conducted on the basis of electroencephalography, with subsequent mathematical analysis.
Indications
- Early diagnosis of memory loss before the onset of the dementia clinic;
- proficiency testing;
- monitoring the effectiveness of treatment for dementia;
- diagnosis of cognitive impairment in epilepsy;
- assessment of the severity of cognitive disorders in children with behavioral abnormalities.
The study can be conducted anonymously on a fee basis, the result is handed out on paper on the day of treatment.
Contact at: Brest, st. Ploska, 17 (psychiatric department of day care).
Additional information and recording by phone: +375-162-55-00-04
